Object types#
The default installation of i-doit already offers a large variety of object types which can be used for a wide range of purposes or can be hidden when they are not used. This article provides a short overview of object types.
| Object type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Access Point Controller | Controls and manages access points | |
| Air Condition System | Air conditioning of active components | |
| Aircraft | Aircraft | |
| Amplifier | Active components for amplifying signals etc. | |
| Appliance | Appliances which are used in the organization but are rather designed as black box | Firewalls |
| Application | End user applications | Web browser, Office applications |
| Blade chassis | Chassis for Blade server | |
| Blade server | Physical server in a Blade chassis | |
| Building | Buildings in a City | |
| Cable tray | Cable routes; see Cable | |
| Cable | A group of wires, such as cupper wires or glass fibers, covered in plastic or rubber and used to carry electricity or electrical signals | |
| Cellular phone | Mobile phones, feature phones, smartphones; see SIM card | |
| City | Cities in a Country | |
| Client | Desktop computers, laptops, workstations | |
| Cluster services | Application for managing highly available systems; see Cluster | |
| Cluster | Logical links of highly available systems | |
| Conduit | Empty conduit for Cable | |
| Contract | Maintenance contracts etc. | |
| Converter | Components for the conversion of signals etc. | |
| Country | Countries | |
| Crypto card | Smart cards with cryptography functions | |
| Database instance | Started instances of a DBMS | |
| Database schema | Created databases of a DBMS | |
| DBMS | Database management systems (DBMS) | MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL |
| Distribution box | For power supply; see Cable | |
| Electric power company | Companies supplying other organizations with power | |
| Emergency plan | Emergency plans as File | |
| Emergency power supply | Systems for power supply when the main power supply fails | Diesel generators |
| FC switch | Fiber channel switches; often in connection with SANs; see Storage system | |
| File | Uploaded files | |
| Host | Remote computers which aren't directly accessible | DNS servers |
| KVM switch | Devices allowing control of multiple input devices (keyboard, video, mouse) | |
| Layer 2 Net | VLANs | |
| Layer 3-Net | Subnets (IPv4, IPv6) | |
| Licenses | Software licenses etc. | |
| Middleware | Middleware is software that lies between an operating system and the applications running on it. | JBoss |
| Migration objects | Objects which had to be migrated after earlier updates (not in use at the moment) | |
| Monitor | External displays for computers; see Client | |
| Net zone | Segmentation of subnets; see Layer 3-Net | |
| Object group | Logical link of objects | |
| Operating system | Operating systems | GNU/Linux, Windows, Mac OS |
| Organization | Companies, institutions, facilities | |
| Patch Panel | Patch panels in a server rack; see Rack | |
| Person groups | Grouped Persons | Access rights groups, departments |
| Persons | People and Bots | |
| Phone | Analog or ISDN telephones | |
| Power distribution unit | Power Distribution Units (PDU) for power supply | |
| Printbox | Printer server | |
| Printer | Printers | Laser printers, Inkjet printers, multifunction devices, fax machines, plotter, 3D printers |
| Rack | Server racks | |
| Remote Management Controller | Components for remote administration of servers; see Server | |
| Replication object | - | |
| Room | Rooms in a Building | |
| Router | Layer-3 router | |
| SAN Zoning | Zones in a SAN; see Storage system | |
| Server | Physical servers | |
| Service | Organizational services provided by an organization | IT services |
| SIM card | SIM cards; see Cellular phone | |
| Stacking | Combination of hardware components | Stacked switches |
| Storage system | Storage Area Networks (SAN) and Network Attached Storages (NAS) | |
| Supernet | Combination of subnets; see Layer 3-Net | |
| Switch Chassis | Housing for modular switches; see Switch | |
| Switch | Layer-2 switches | |
| System service | Services, daemons and applications which are executed on servers | Apache webserver, i-doit, PHP |
| Telephone system | Telephone systems | |
| Uninterruptible power supply | Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) | |
| Vehicle | Vehicles | |
| Virtual client | Virtual desktops; see Virtual host | |
| Virtual host | Host systems for virtual machines; see Virtual Maschine and Virtual client | |
| Virtual Maschine | Virtual machines (VM); see Virtual Host | |
| VoIP telephone | SIP capable telephones | |
| VRRP/HSRP Cluster | Highly available routers which use VRRP, HSRP or CARP protocols | |
| WAN | External connections/ uplinks | |
| Wireless Access Point | WLAN APs | |
| Wiring System | Logical wiring; see Cable | |
| Workplace | Logical links of terminal devices and a person to workplaces |
Fields in the Configuration#
The following fields are displayed in new and existing object types:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
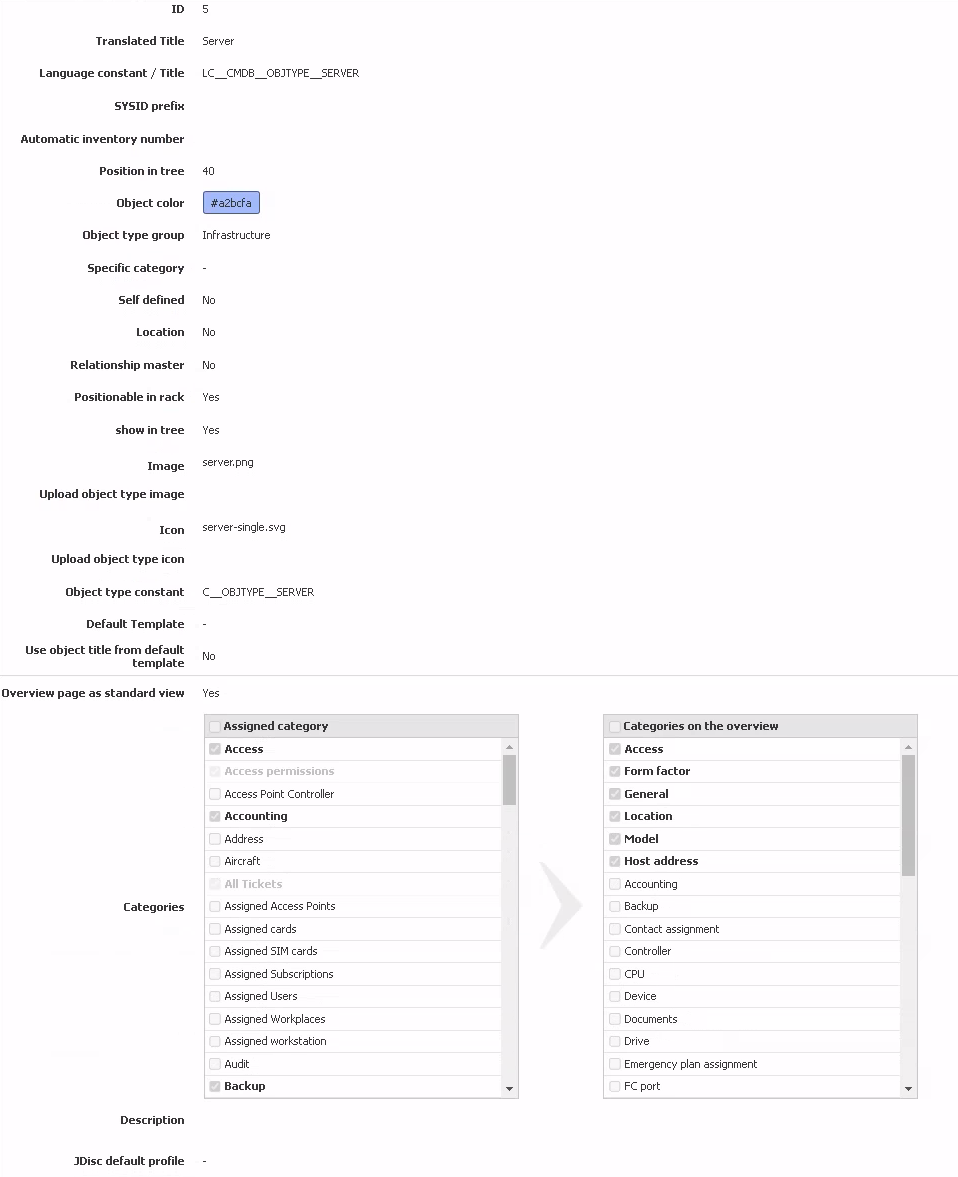
| ID | The ID is a sequential number which is given by the system. Its uniqueness allows for the identification of the object type. A manual change is not possible. |
| Translated Title | Using this field you can check whether the language constant you are using is correctly translated in the currently chosen language if you are using your own language file. |
| Language constant / Title | It is possible in this field to enter a language constant or a title in plain text. If you are using i-doit multilingual, please use a constant you translate in your own language file. |
| SYSID Prefix | The SYSID prefix is inserted in all objects of this type when generating the SYSID. When leaving this field empty, the standard prefix SYSID_ will be used. Otherwise, the SYSIDs will be generated with your own prefix. If the field remains untouched, the current Unix timestamp will be included in the SYSID. The object ID is included for custom prefixes. |
| Automatic inventory numbers | If you want i-doit to generate individual inventory numbers on its own for objects of this type, you can enter the formula for this here. Variables are available for this which you can display via the blue question mark at the end of the line. It is also possible to combine these variables with each other and with plain text. |
| Position in tree | If you are not using an alphabetical sorting for the object types in the tree menu on left side, you can create a custom order via the sorting. The sorting takes place in ascending order based on the number values. |
| Object color | Here you can assign a color to each object type. These color tags are found for example in theCMDB explorer and also in the graphical representation of racks to make the display more transparent. |
| Object type group | If you changed your mind while configuring and assigned your object type to another group or if you wanted to move an existing object type in another group, you can adjust the object type group via this option. |
| Specific category | You can optionally choose the desired specific category and link it with the object type using a drop-down menu. Please note that specific categories are mutually exclusive and therefore only one specific category can be chosen. |
| Self defined | The Custom information will inform you whether this object type is already available in the standard installation or if it was created by a user. Standard object types can only be hidden and not be deleted. |
| Location | In this selection it is possible to define whether objects of this type are supposed to serve as the physical location for further objects. Objects which are not supposed to serve as the physical location will not be shown in the location browser. |
| Relationship master | Each object relation has a direction or a dependency. When editing an object and linking another, the linked object is always dependent on the object being edited. However, if the linked object is an object whose object type has been configured as relation master, this object will then assume the master role in the relation. |
| Positionable in rack | Here you can declare whether objects of this type can be built into a rack within specific height units. When deactivated, the attributes are not available for positioning in the rack. |
| show in tree | The display in the menu tree can be deactivated with this option. If you don't need standard object types and want to hide them or if you don't want your custom object types to appear in the menu tree yet, you can hide them for all users here. |
| Image | Here you can select a standard object picture for the information line. |
| Icon | With this option you can determine the icon that will be displayed next to your object type in the menu tree. For this you need to specify the path of the icon beginning from the_i-doit_installation folder. |
| Object type constant | You can determine a Object type constant which allows database queries for the object type. In_i-doit_the standard formula for this is C__OBJTYPE__[NAME], while [NAME] is to be replaced by the name of the object type._i-doit_automatically generates a constant which receives the current Unix timestamp instead of the name. Replace the Unix timestamp by the stylized name of the object type (ideally only ASCII capital letters) for better readability (e.g. for SQL reports). |
| Default Template | If you already created templates using the template feature, you can select a template here which is then used to fill in new objects automatically. This way, you can pre-fill values which are the same for all objects of this type. You can adjust these pre-filled values anytime, if needed. |
| Default Template | If you have already created templates with the Template function, you can select a template here according to whose template new objects are automatically filled. You can set the same values for all objects of this type. You can change these values if necessary |
| Use object title from default template | If you have already created templates with the Template function, you can select here whether the name of the object should be generated via the template |
| Overview page as standard view | With this option you determine whether opening an object of this type will display the overview page or the category General. This option is set to "No" by default. When setting it to "Yes", the selected specific category will be added automatically to the overview page. |
| Categories | You customize your object type in this selection. Each category having its checkbox activated will be available within your object type. In the right column you can specify what categories will be shown on the overview page. This selection is only possible if the overview page was previously set as the standard display. The order of categories can be determined per drag'n'drop using the hatched lines. |
| Description | Here it is possible to leave hints and notes regarding your object type. |
| JDisc default profile | If a JDisc Import Profile has been created, this can be selected here. This JDisc import profile is then preselected in the JDisc Discovery category. |
As soon as your configuration is complete, you can save your settings using the Save button.