Search#
"Seek and you shall find." Specific research in the IT documentation requires a fast and comfortable search. A specific search is often a faster method than clicking through menu structures.
The Search Field#
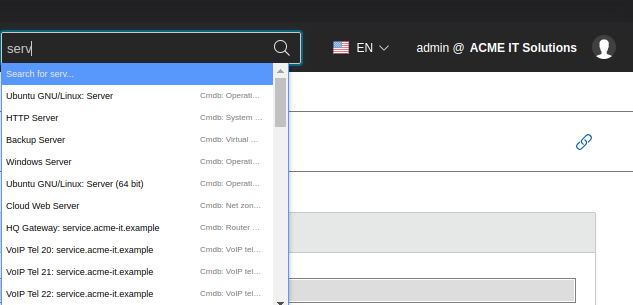
The search field is located in the web GUI of i-doit in the upper right corner. Here you can search for any term of the IT documentation. While typing, the first results already appear (search suggestions), they can be selected using the mouse or the keyboard (auto-completion) to jump directly to the found data set.
Apart from the plain text, the search can be restricted to specific object attributes:
- If the search begins with a hash followed by the object ID (#123), the overview page of the object associated to this ID will be opened upon pressing the return key.
- If the search begins with the keyword title followed by a colon and the object title, the corresponding object will be displayed (title:acme).
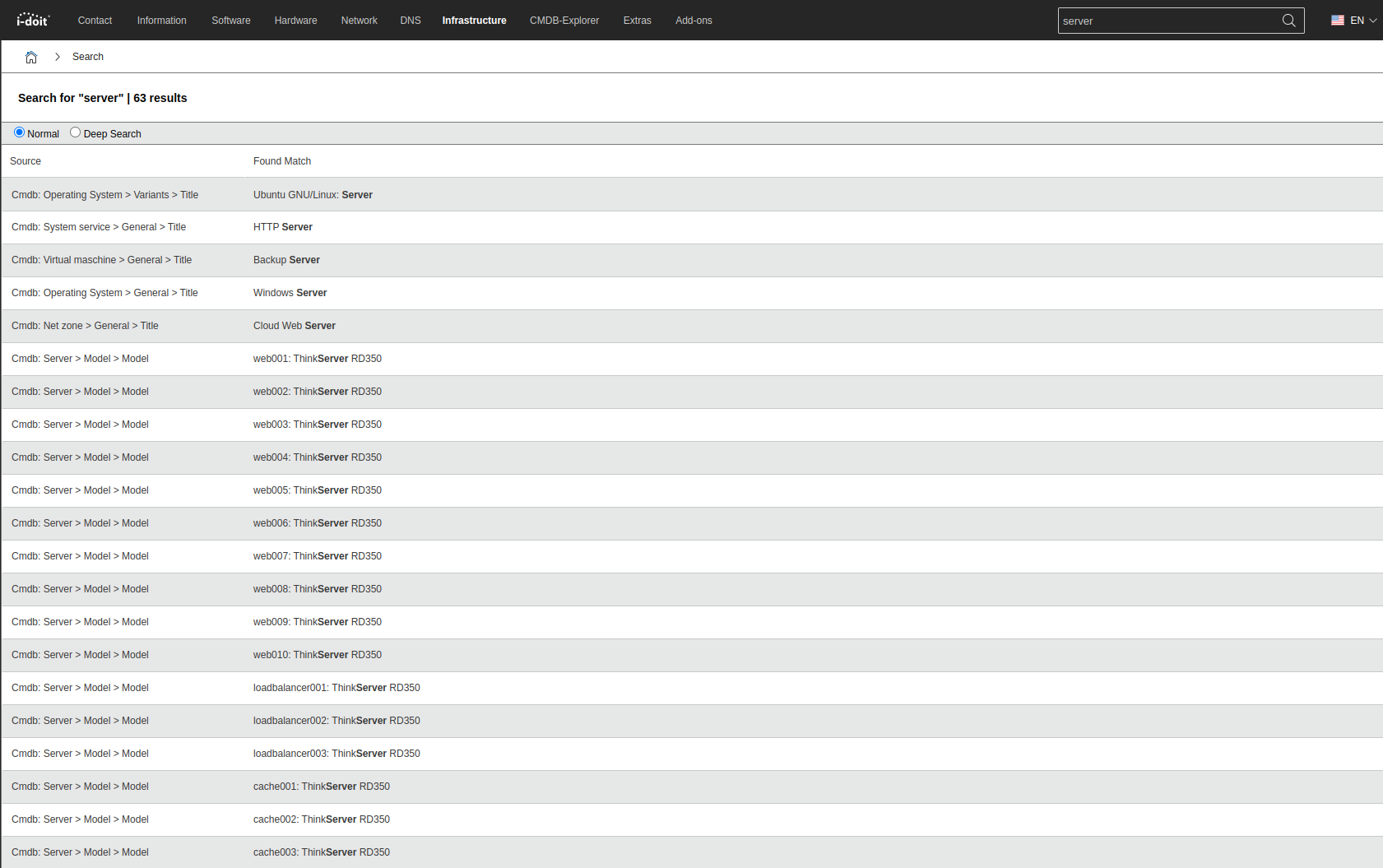
The Search Results#
If the search suggestions mentioned above do not lead to the desired result, then pressing return will present a page with search results. Next to each piece of found data sets also the source is stated, for example, the attribute of a category of an object type in the CMDB module.
Set bookmark/favorite
Each search can be referenced via the URL. Searching the term "acme" results in the URL http://i-doit/search?q=acme. Search results can be saved as bookmarks/favorites in the web browser in order to be able to access them quicker.
Search Mode#
There are two selectable modes for the search which all may lead to different results:
- Normal: The indexing (see below) is used for the search. This is the default setting.
- Deep Search: Attributes are scanned one after another. The index is ignored. This search mode takes more time than the others.
The search mode can be selected at Extras → CMDB → Search after the first search. At Administration → [Tenant name] management → Settings for [Tenant name] → Search → Default search mode you can select the specific mode you want to use automatically in the future.
Automatic Deep Search#
Should a search with the predefined mode (see above) provide an unsatisfactory result or even no result, you can carry out a Deep Search automatically. You can configure the settings for Deep Search under Administration → [Tenant name] management → Settings for [Tenant name] → Search → Automatic DeepSearch:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Active | The search results are supplemented by an additional Deep Search. |
| Active, when no results are found | The additional Deep Search is started when there are no results. |
| Deactivated | The additional Deep Search is omitted. |
Indexing#
Initially, the search index is generated automatically when updating or installing. Only for very big databases with more than 500,000 objects it has to be generated manually to ensure that the search is fast and delivers good results. The index can be created or updated in the background regardless of user interactions. This action is triggered via the i-doit Console. An example call and explanations of the possible parameters can be found in the corresponding article.
1 | |
Alternatively, the Reindex can also be executed in the i-doit administration at Repair and clean up up via the Re-new search index button.
Memory requirement
On a Unix-like operating system the index is 500 MB per 1 million indexed data records. Usually, the duration of a search query is not increased by bigger indexes.
Search via the Console#
The CLI tool allows you to search via the command line. An example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
Search via the API#
It is also possible to search the IT documentation via the Application Programming Interface (API) of i-doit. The required method is idoit.search:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
The server replies as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
Adjust the Indexing#
The indexing of i-doit utilizes many features that are provided by MySQL/MariaDB. These can be customized. For some settings the configuration file of MySQL/MariaDB is adjusted (for example at /etc/mysql/conf.d/i-doit.cnf). For other settings it is required to run SQL statements for which the command line client is suitable. Example:
1 | |
Word Length#
An important question for indexing is how long the minimal length of a word has to be. Often this value is set to 3 characters. Terms like "PC 01" will not be found with this value. A suitable specification would be a value of 2 or even 1 character(s).
1 | |
This setting could lead to an index which is many times greater than before.
Word Separators#
In order to differentiate between words, various characters are used to serve as separators (e.g. space, dot, dash). To find the term "PC-01", the term is separated into "PC" and "01". The word length is again the decisive factor whether "PC" and "01" are indexed or not.
Stop Words#
Stop words are the terms which are ignored when searching. Thus the index should not take these words into account. Examples for such words are "at", "that" and "with". MySQL already provides a list of stop words which is relatively small, however, and only contains English terms. This list can be replaced by your own list. You can use the following SQL statements:
Enter the system database of i-doit:
1 | |
If the table does not exist yet, it should be created:
1 | |
Empty the table#
1 | |
Insert list of stop words:
1 2 | |
Lists of stop words in various languages can be found on the internet.
The following settings are required to replace the MySQL list with your list:
1 | |
Activate Index Changes#
Three steps are necessary to make changes to the index behavior effective. First you should restart the MySQL service. The following command is used for Debian-based operating systems:
1 | |
Afterwards, the following SQL statement has to be run for each tenant database:
1 | |
Complete SQL statement for the first tenant with the database idoit_data:
1 2 | |
Finally, re-indexing via the i-doit controller has to be effected (see above).
Increase the limit of 2500 results#
If objects are named consecutively e.g. 123456-00001 to 123456-99999 only objects up to 123456-2500 can be found with normal search settings.
This limit is for performance reasons. To increase this limit, an expert setting must be added.
Here is an example where the limit was set to 5000 results.
| Key | Value | Type |
|---|---|---|
| search.limit | 5000 | Tenant-wide |