IP List#
Again and again there is one central issue for the Admin: Which IP addresses are assigned to which host and which addresses can still be assigned? The IP lists in i-doit can be a great help to tackle this question.
A more detailed approach into this matter is provided in the application case for the IP Address Management (IPAM).
IP List Category#
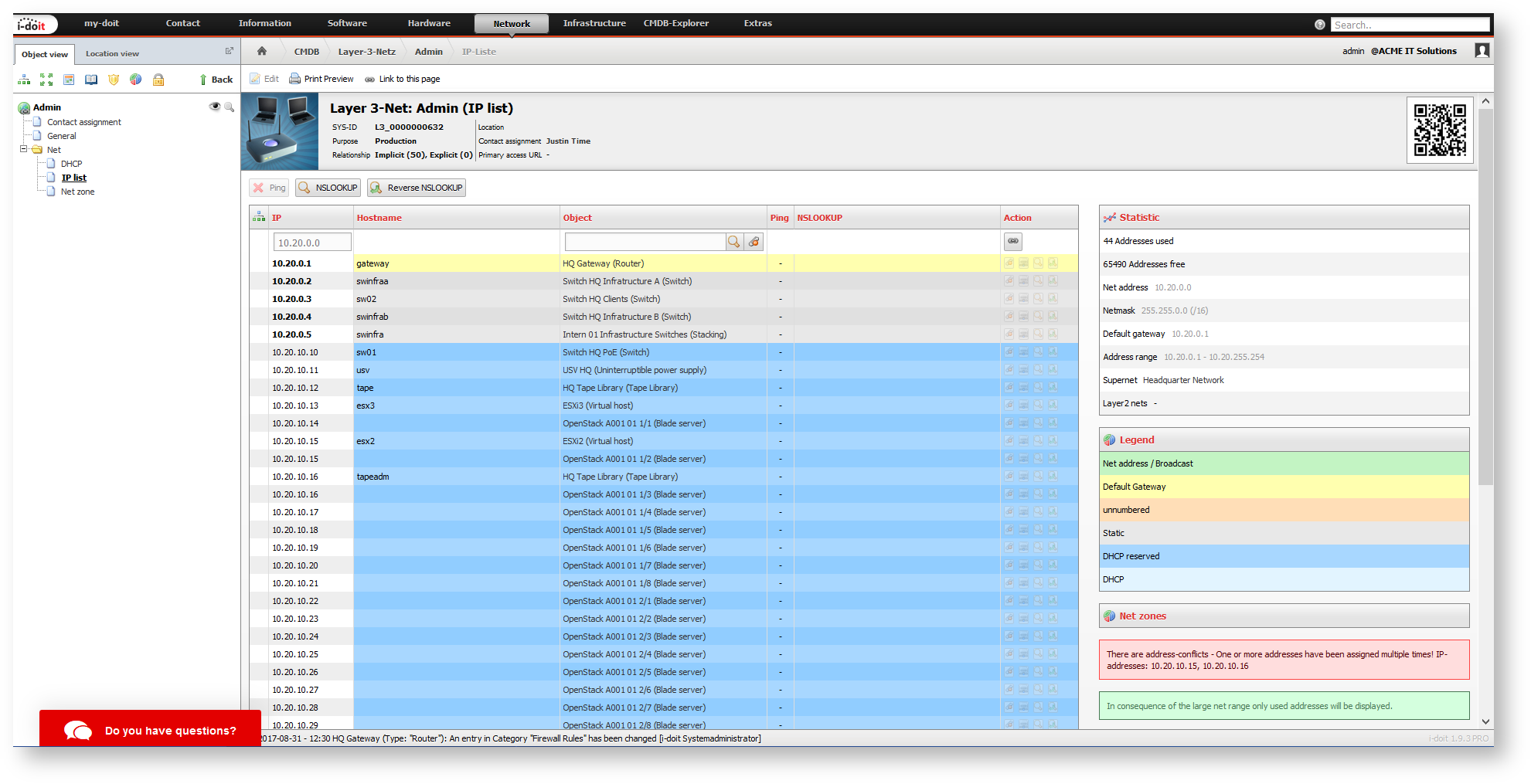
The IP list category provides a comprehensive overview of each net. In the default installation of i-doit it is assigned to the object type Layer-3-Net. You can find all objects which are assigned to this net, including their IP address, host name and type of address assignment, in a tabular listing.
The type of address assignment is presented with colors and their respective meaning is explained in a color key on the right of the list:
-
Green:
Net address / Broadcast -
Yellow:
Default Gateway (This is the object for which you defined in the Host address category that it should act as default gateway.) -
Orange:
unnumbered address range -
Gray:
statically assigned IP addresses -
Blue:
IP addresses which are reserved by the DHCP server (see also DHCP category) -
Light blue:
IP addresses which are assigned dynamically by the DHCP server (see also DHCP category)
In order to avoid (unintentional) address conflicts, i-doit points out multiple assigned IP addresses beside the table.
In smaller networks (< 1,000 IP addresses) also IP addresses which have not been assigned yet are displayed. Should the network have an address range which is too extensive, for example a /16 with more than 65,000 IP addresses, only the used IP addresses are shown and those who are not yet assigned are hidden. Additionally, a corresponding note is made.
Another table on the right concludes important information about the net:
- IP addresses in use
- Net address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- Address range
- Superordinate supernets (object type Supernet)
- Assigned VLANs (object type Layer-2-Net)
Object Assignment#
You can expand the list by further objects without using the Host address category but by using the Connect object button.
Check of IP Addresses#
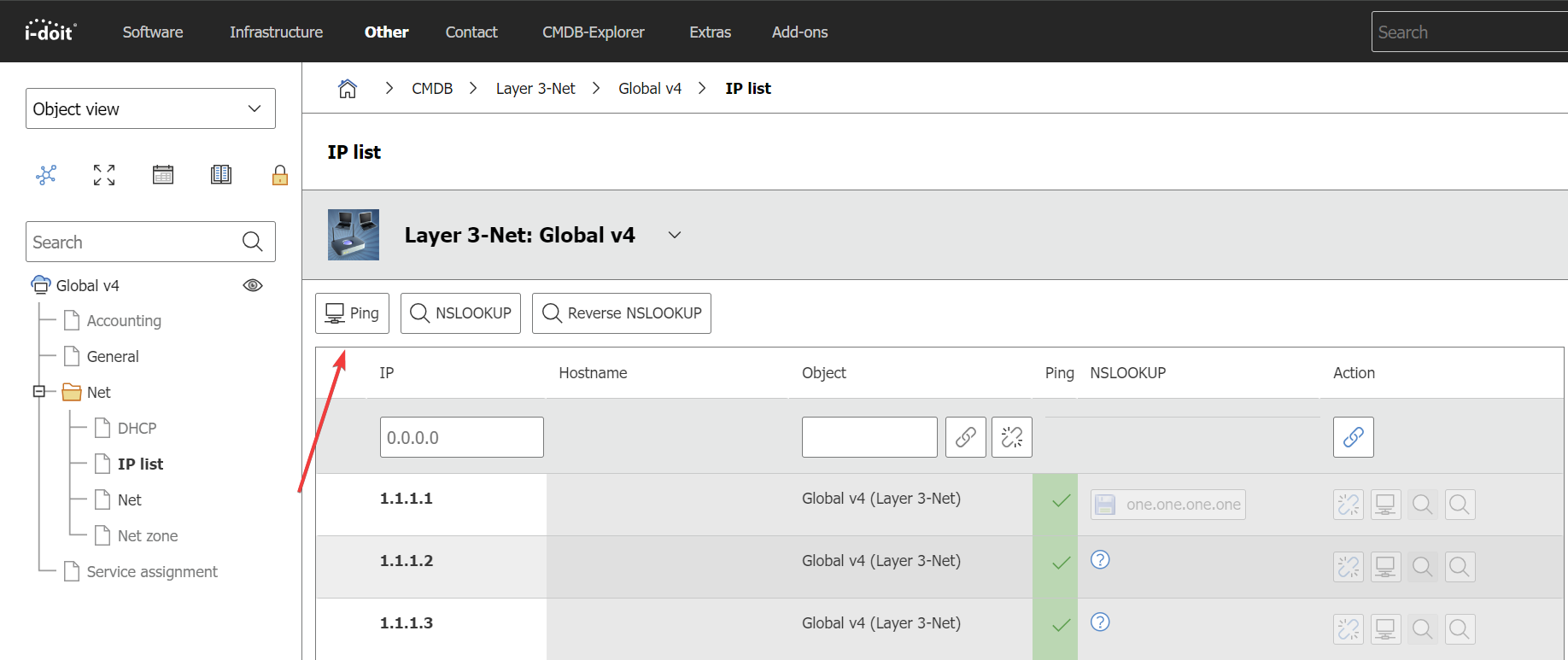
The IP list category provides the possibility to make a comparison between the target state and the actual state. In order to check if the documented IP addresses and host names are really assigned, i-doit can send ICMP packets ("Pings") and start a NSLOOKUP. For this purpose, i-doit requires net access. You can check single entries or all entries in a subsequent order. With Administration → System settings → Tentantsettings → Options for the IP-List you can set which command line tools should be applied. The user/ group of the Apache webserver have to have the permission to activate these tools.
- Ping: Send ICMP packet to IP address
- NSLOOKUP: Specify IP address as host name
- Reverse NSLOOKUP: Specify host name for IP address
Nmap Installation#
Windows#
Download the latest stable version of Nmap on https://nmap.org/download.html and run the setup.
If for some reason you cannot download it directly, you can use the CLI.
Open Command Prompt and use bitsadmin to download the Nmap Zip archive:
1 | |
Currently the last zip file is not the latest stable version.
Once Nmap is installed, add the Nmap directory to the system PATH environment variable
1 | |
Ensure the path matches the directory where you extracted Nmap
Unix#
Debian or Ubuntu#
1 2 | |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)#
1 | |
or
1 | |
IP List Ping#
Once Nmap is installed, you will find the "Ping" Button available